Weboldalamat a háttérben folyamatosan újítom, javítgatom! A már meglévő tartalom, és funkciók változatlan formában elérhetők és használhatók. My website is under maintenance. You can still use the existing functions and content.
Things you should never do during a thunderstorm! Zoltan Csengeri's lightning safety page.
Introduction
How do thunderstorms develop?
Main sources of lightning are cumulonimbus clouds which are developed from the hot and humid air raising from the ground in the summer. Clouds can have infinite variations of shape but meteorolgy divides cloud formations in 3 categories: cirroform, stratiform and cumuliform clouds:
- Cirroform clouds are at or higher than 5 kilometers altitude, its "long threads" are formed by ice crystals. These clouds are mainly connected by approaching warm fronts.
- Stratiform clouds are mainly at about 2-5 kilometers, they are mainly developed by winds and connected to fronts (mainly warm fronts). If they are very thick, they can cause rain or snow but not lightning.
- Cumuliform clouds appear from the 600 meters altitude and can rise up to 15 kilometers altitude. They are the main sources of lightning storms.
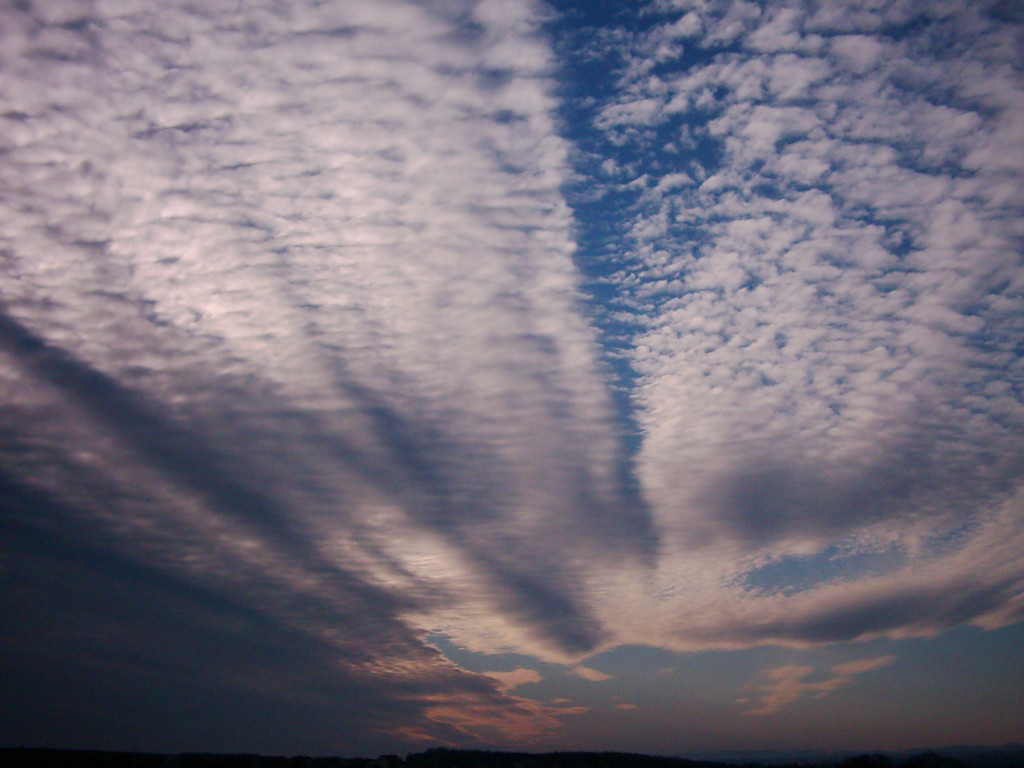



In the beginning, cumuliform clouds are flat from sides, but from below, they look like cotton. Their meteorological name is cumulus humilis.


Animation video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PRD0W0kJgNE
In the cloud development, humidity, temperature and pressure play important roles. These clouds are made of tiny fluid water droplets. They have a very short life-cycle, they disappear 5 minutes after appearing.
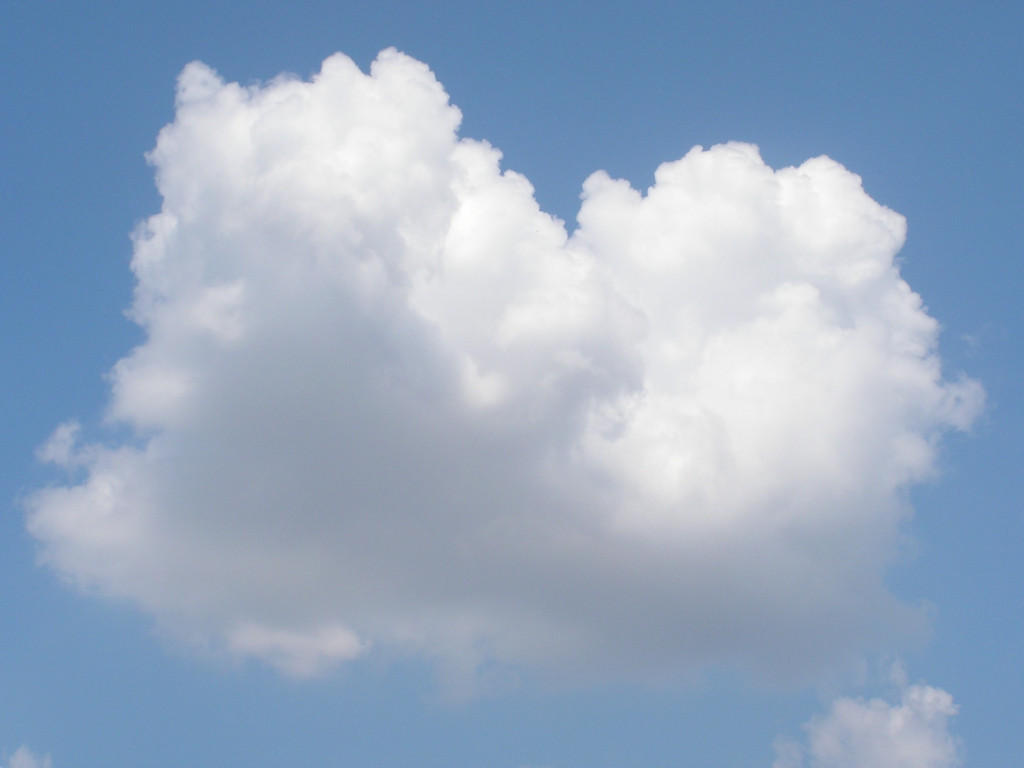


Animation video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3D243e2f1s
As humidity level of the atmosphere rise and the temperature of the upper layers of the atmosphere falls (temperature difference between lower and higher regions rise) the clouds growing larger and you now can see the cauliflower shapes of the cloud tops. This is now called cumulus mediocris. However the temperature of the clouds fall to the temperature of the surrounding air, this means the updraft run out of force. The remaining humidiy makes the cloud heavier than the surrounding, so it falls back a little and its humidity evaporates back into the air. These clouds still don't exist longer than 15-20 minutes.
If moisture of the air is raising and the upper atmosphere temperature is falling even more, cumulus clouds will tower to even higher altitudes, they become cumulus congestus. And something else will be happening: All of the clouds create their own flow system in the atmosphere. Huge vortices appear and these will sometimes weaken, sometimes strengten each other. The cumulus clouds are a very little visible parts of these vortices.
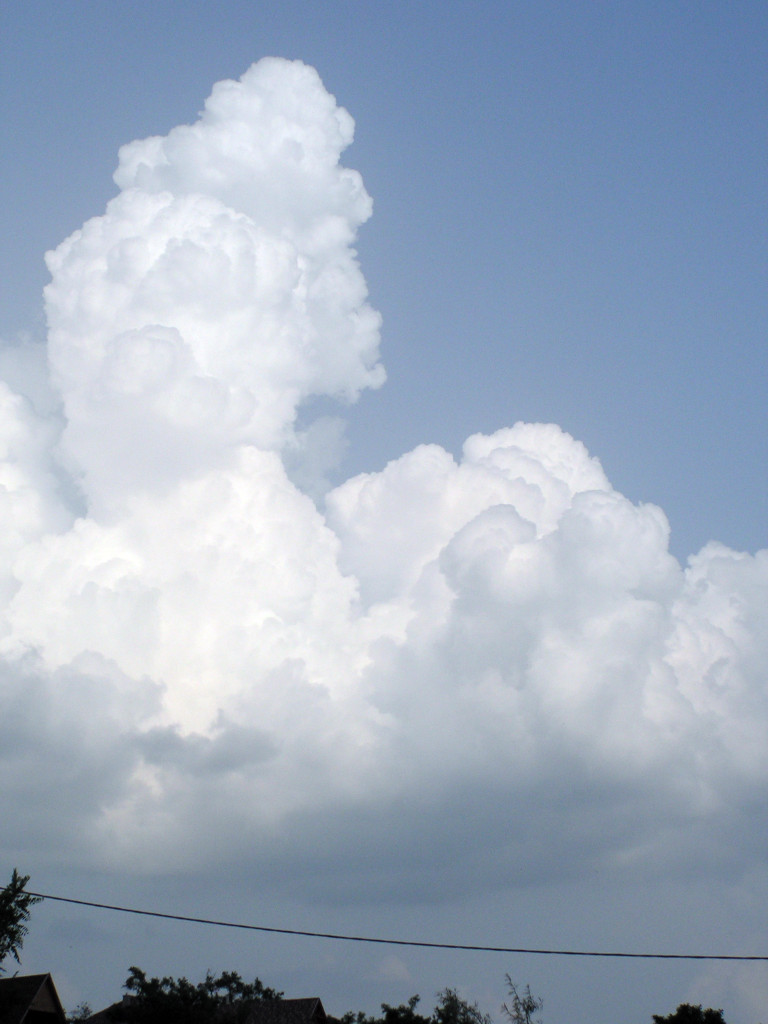
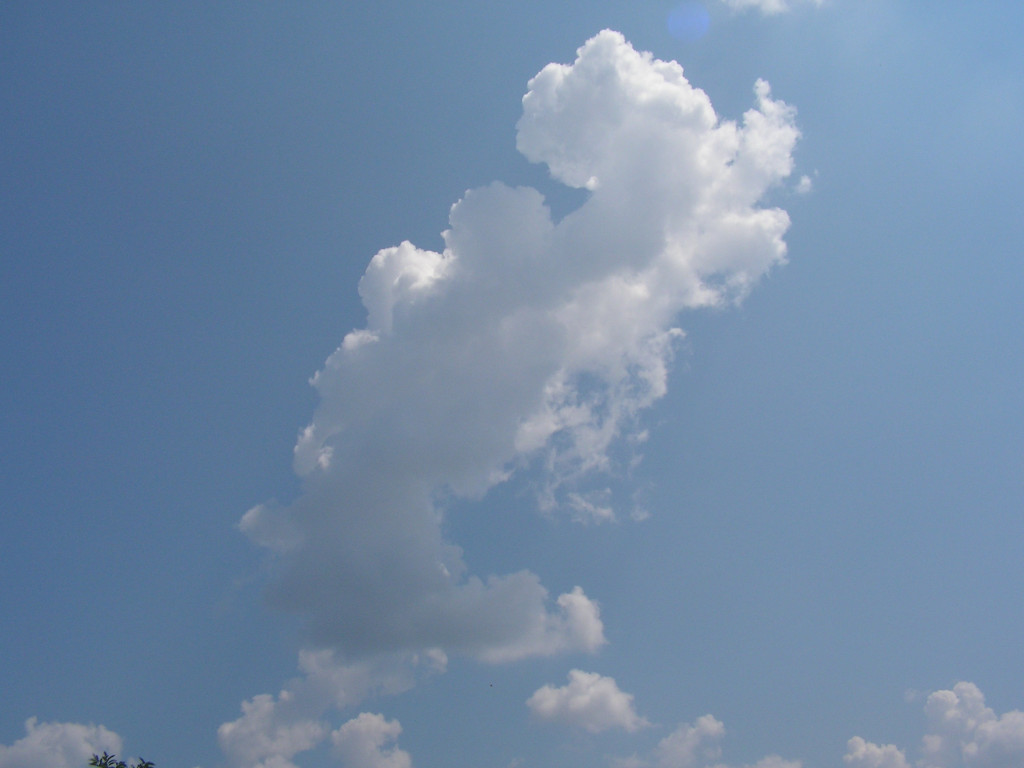


From this time, cloud development is supported not only the warm moist air updraft from the ground but by these vortices and even by the cloud development itself as well. Cloud development is condensation (the steam becomes fluid water) which releases latent heat and this additional heat make more air raising up. From this time clouds won't disappear, but a chain-reaction is beginning that supports clouds with even more heat and moisture from below. Below the cloud, air pressure lowers and people who staying there will experience effects similar to the warm fronts. This is the typical 'calm before a storm' period.
Looking up to the sky, you will see huge 'cauliflowers', columns of cumuli and thickened clouds. The storm is now about to break: one of the clouds is being launched with the speed of more than 100 km/h!
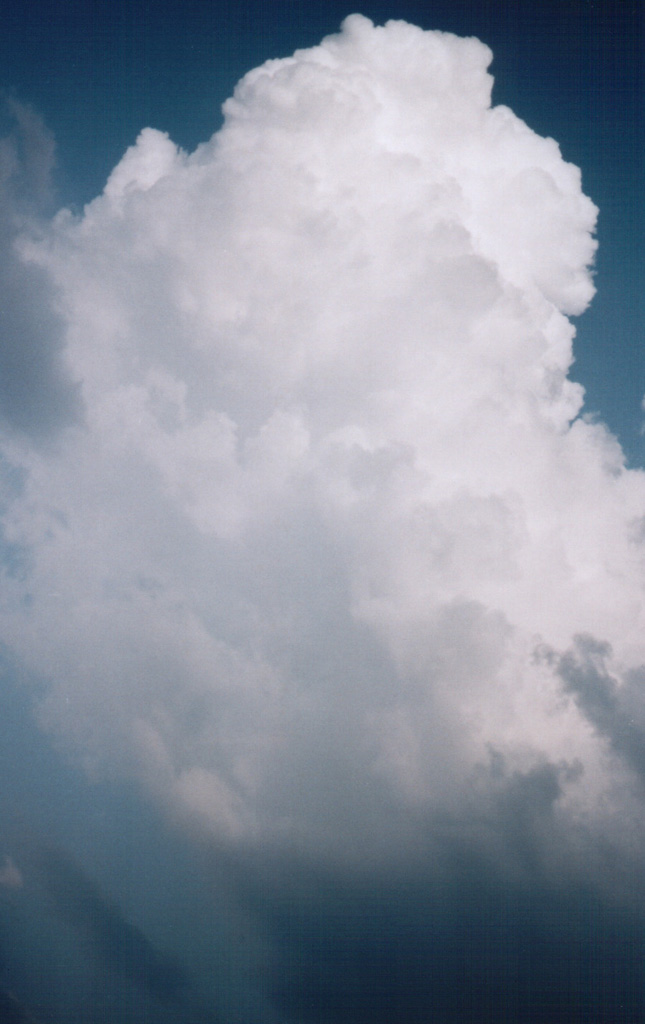

The top of the cloud hits the tropopauza and now contains ice crystals instead of water droplets. This is called now cumulonimbus, thunderstorm cloud
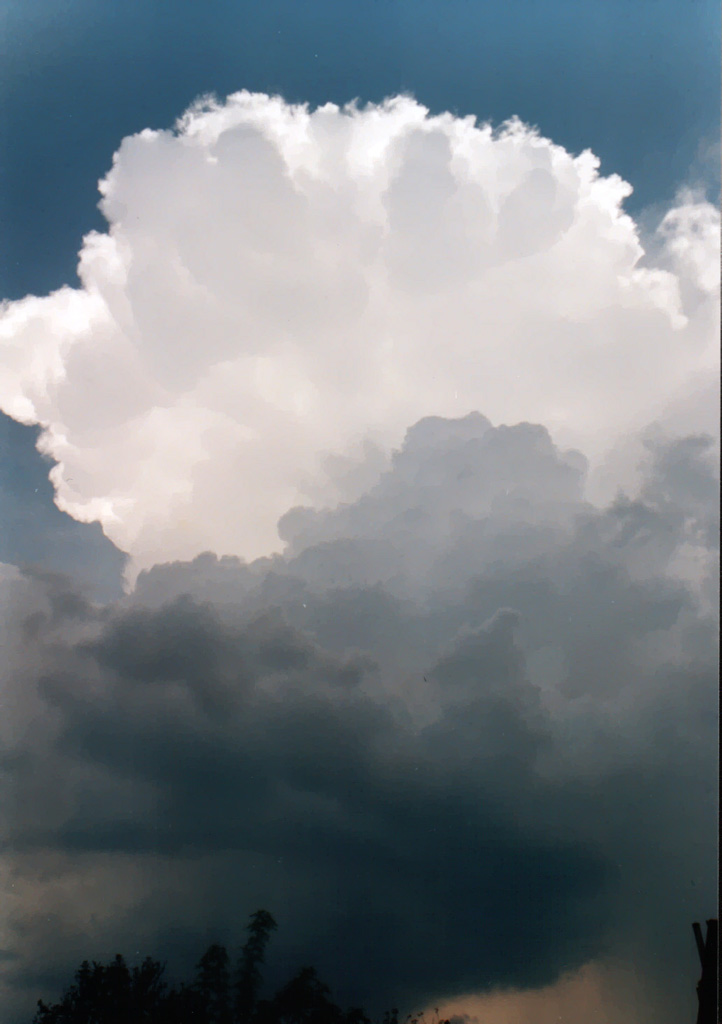

The top of the thunderstorm spread off in every direction. At first the cloud is shaped like a mushroom, later is shaped like an anvil. The ice particles inside the cloud will coheres to each other, becoming larger and larger until they fall into the updrafting water droplets. Hitting and rubbing each other makes they get electrically charged. Everything is ready to the lightning! You can read about the lightning here. Scientists still don't know exactly what the initial moment of the lightning strike is. Today, they say cosmic rays from star explosions (supernovas) are responsible for it. But in my opinion this theory can't explain lightning inside the 200-300 meters high volcano cloud columns!: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6gW-Txy8pmc
Forecasting thunderstorms
Before a long time, people 'forecasted' storms by observing animals, clouds and their own behaving. Today information technology, supercomputers can predict when and where will be storming for a couple of days. In Hungary, mostly used meteorology models are: AROME model of Hungarian Meteorology Service http://www.met.hu/idojaras/elorejelzes/modellek/AROME/, the Polish Unified Model: http://www.meteo.pl/, (forecast modell with 1.5 km details): http://maps.meteo.pl/), the German ALARO ZAMG modell: https://www.zamg.ac.at/cms/de/wetter/wetteranimation and the German WRF ARW: http://www.modellzentrale.de/WRF/index_en.php There are more forecasting models with smaller detail like GFS that can help predicting thunderstorm periods and massive storm-producing cold fronts: http://www.wetterzentrale.de/topkarten/fsavneur.html
Avoiding lightning strikes
Although the modern technology and reliable weather forecasts, there are still 1.000 people suffering lightning strikes in a year and half of these accidents ends in death! In most cases victims die because their heart stops working or they drown due to sudden muscle cramps. These accidents could have been avoided by watching themselves, knowing what not to do in a storm and not following always the bad old habits! Lightning photos and thunderstorm videos actually tell you the most dangerous periods and parts of thunderstorms: Most lightning strike near the edge of rainfall but at the earlier stages of the storm, lightning strikes from the every part of the cloud! So, all in all, if you can hear thunder, the storm is dangerously close to you!
There are many activities you do day by day that are as dangerous as standing an alone and tall tree in a thunderstorm! I highlighted these with bold letters
- You have to escape open areas before the storm outbreak (at the time of calm before storm)! Hide inside a building or a closed car (not convertible). Pull the windows up and don't touch the metal body! If you are in the water, run to the land!
- Public utility wires and pipes are good conductors of electricity. Never use landline phone! It is very late and dangerous to unplug electric devices when it is thunderring, if you haven't done it already, leave them inside the power supply! Do not use desktop PC! If you have a laptop, use the WIFI or rather satellite internet! You can use your smart phone! Your computer must not connected to the HIFI Stereo system! Use your headphones by plugging it into the laptop, but not the HIFI system! Do not use massage or trainer devices (treadmills, indoor cycles, massage seats) that are connected into the power supply.
- Do not dishwash or take bath, shower! Do not use water from the tap and don't touch water pipes!
- If you got stuck in a forest, lower trees are a little safer than the higher ones!
- If you have no chances, go to the lower places, pits! Throw away fishing lines, tennis rackets or other long metals! Avoid trees and power lines! Do not use mobile phones! It creates electromagnetic field that can attract lightning!
- Do not fly quadrocopters, drones! Drones above you could be a step point of lightning toward you.
- You need to extinguish fire that you set for cauldroning! The flames of fire and smoke are good electric conductors and can attract lightning like a tall tree! Avoid pot holes, caves, channels and other places from where gas can leak out!
- If you are in a city and waiting for a bus in a bus stop, don't touch the body of the bus waiting (neither the metal, nor the glass!) Do not take off when you are on the bus or a tram especially places from where there's nowhere to hide within 20 meters! Hide inside a building instead of subway station! Almost everything is dangerous (trees, pillars, fences, traffic signs and lights, tram or trolley wires and ponds).

False legends!
- Many video recordings and photos proved the opposite of this:
Lightning does not strike twice to the same place.Lightning doesn't strike tall buildings in the world twice but at least 20 times! - Lightning protector plugs: Lightning protector plugs are very common nowadays but they won't save your systems from direct hits only the secondary strikes (current inducted from electromagnetic pulses) Even life protector relays won't shield them from direct hit! Lightning protector systems are the only way to shield your house from lightning!
Opened Both the doors and windows can lead lightning into house.Never heard of any evidence about this but ball lightnings can enter the house, even through closed windows and doors.- There's no safe place outside! I heard from elderlies you need to lie prone on the ground. Nowadays people say you need to squat on toes and put your hands on your head. Whatever you do, you aren't safe neither from lightning current nor from secondary ground current caused by a close lightning strike!
- No lightning from clear sky: Except if there's a thunderstorm cloud nearby, lightning can strike 20-25 kilometers away from the cloud!
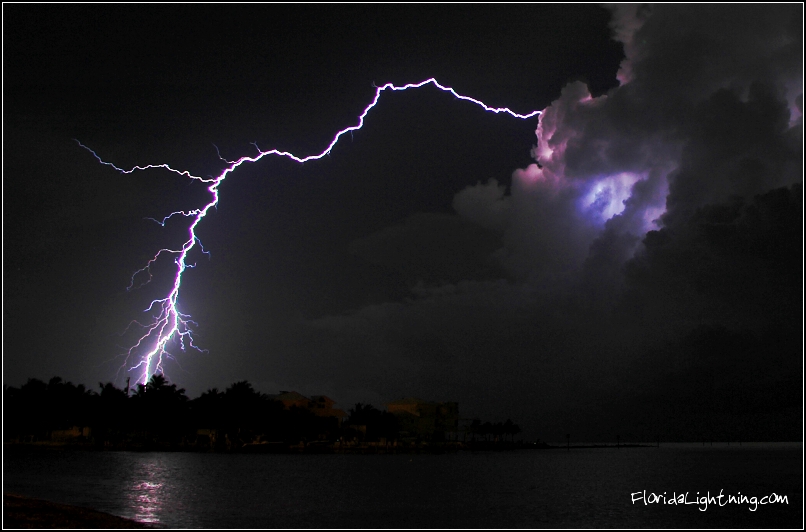


Forrás: www.lightningsafety.noaa.gov
What to do when someone has been struck by lightning?
- You can touch him, because they are not charged electrically.
- Call 911.
- The injured suffered electric shock, his or her body burnt the enter and the exit points of lightning.
- Lightning can cause permament damage in nervous system, broken bones, sight or hearing loss.
- Steps of first aid are valid at this time too. Ensuring breathing and heart massage if necessary.
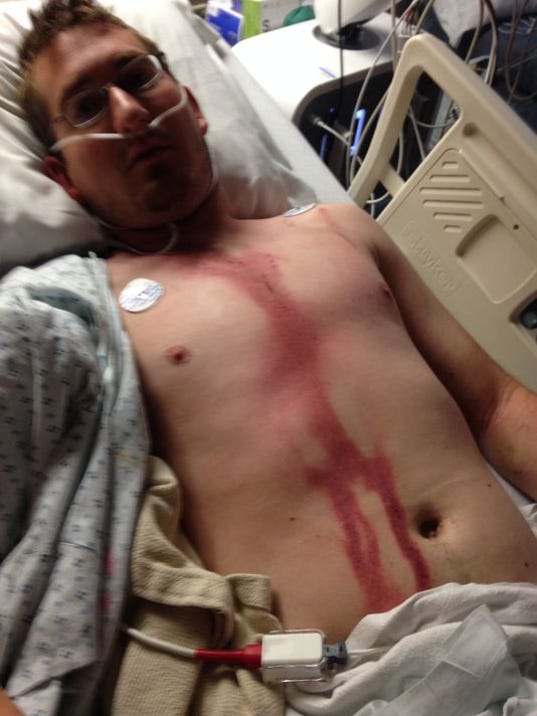
Lichtenberg-figures will be permamently on the victims' skins after lightning strikes.

Lightning and electric accident mysteries
Lightning strikes (and even other kind of electric accidents) can give scientificly unexplained abilities to the victims. There are cases when people 'healed' injuries suffered from an earlier accidents: Edwin W Robinson lost his sight and hearing in a car accident, but after a lightning strike, he can see and hear again! Physicist György Egely told that one of his own job interviewees suffered electric shock. And after the shock his conscious could leave his body and enter there again as many times as he wanted.

